The Ministry of Energy, Trade and Infrastructure endorsed Mitsui and Stem in a competitive solicitation to develop distributed Virtual Power Plants (VPPs) for grid benefit.
The companies will initially deploy more than 750 kWh across multiple sites to form a distributed resource. This pilot will help inform Japan’s plans to develop aggregated demand response resources as flexible capacity to manage the variability from increased renewable energy resources on the grid.
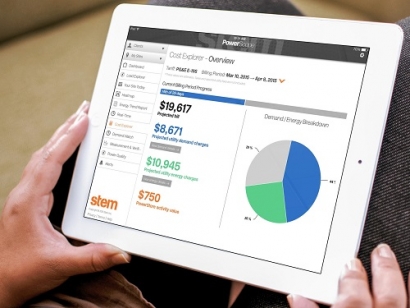
Stem’s predictive analytics and machine learning, coupled with its Power Monitor and Powerscope user interface tools, provide the data and analytical insights needed for robust facility energy management. Stem captures energy data on a one-second basis, dispatches on a five-minute basis, and stores terabytes of data to the cloud.
METI will be testing deregulated services and markets as Japan undergoes a dramatic redesign of the country’s nearly-300 GW electricity market. The restructuring will promote renewable energy and help modernize the Japanese electric grid by introducing competitive services and flexible resources. Japan’s dense urban areas cannot easily accommodate additional generation resources, making customer-sited virtual power plants that leverage the real-time balancing and intelligence offered by energy storage particularly important.
“Mitsui selected Stem to deploy intelligent energy storage and analytics for customer and grid benefits around the world,” said John Carrington, CEO of Stem. “Japan is poised to dramatically scale its demand response market, and we are proud to have Mitsui as a development partner and investor.”
The initial sites within the virtual power plant network are the first of planned projects in Japan for Stem and Mitsui and a base for further Asian expansion.
Photo courtesy Stem

